|
hc8meifmdc|20005939267D|healthm_live|health_library|health_library_details|0xfdff55bd010000001101000001000700
| Contents |
| |
Legendary of Astaxanthin
What is Astaxanthin?
What is the unique advantage of Astaxanthin in the family of Carotenoids?
Sources of Astaxanthin
Different value of Astaxanthin from different sources
Natural source of Astaxanthin --- Extracts of Haematococcus BioAstin®
Efficacy and characteristics
Function and mechanism
Range of application
Practical application
Patent
Products
FAQ |
| |
Legendary of Astaxanthin
In 19th century, a French explorer who was traveling in Nova Scotia Province of Canada, he came to the Bras d’or Lake on the Cape Breton Island for exploration. The lake belongs to a natural salt lake in frigid zone and the salinity is extremely high. Under such a severe condition almost no creature could survive, however, to the explorer’s surprise, there was one sort of small red worm actually living in this barren lake. What is the magic power which made the small worm survive under such a condition? It made the explorer very interested.
Then scientists began to research this worm further and a natural anti-oxidant was discovered in the worm’s body, it was Astaxanthin. The small worms were protected just by Astaxanthin for survival.
At the beginning of 20th century, a better source of astaxanthin --- Haematococcus pluvialis was discovered by the scientists.
The life history of this magic alga through a red resting stage and green swimming stage followed again by a red resting stage. The red substance in the alga is astaxanthin.
Haematococcus is considerably better suited for survival under conditions of expeditious and extreme fluctuations in light, temperature and salt concentration than most algae, due to its rapid ability to encyst. In a clean environment where the nutrition is sufficient, the red alga will be in green swimming stage. Once the environment becomes worse, it could translate to be the red cysts which have resistance and astaxanthin will be accumulated, now it is in its red resting stage.
It seems that some creatures in the nature could be survived by astaxanthin under harsh conditions, what about our human beings with a wise brain?
What is Astaxanthin?
Astaxanthin, is a kind of carotenoids, the chemical name is 3,3"-dihydroxy -4,4"- diketone -ß-carotene, the molecular formula is C40H52O4 .
Astaxanthin is a red carotenoids which could be found in the shell of shrimp, crab, oyster, and in the body of salmon, alga and fungi. In most circumstances, it appears as fresh red or orange in color. However, in the body of some shellfish, such as shrimp and crab, it could become dark blue or green due to the combination with protein. During the processing (e.g. cooking) it could recover its red color since heating will ruin the combination of astaxanthin and protein.
Astaxanthin is a multifunctional substance which could eliminate free radicals, protecting blood vessels, lowering the cholesterin content, whitening the skin, anti-wrinkle, anti-cancer, protecting eyesight, releasing the pain of joints etc. Moreover, its efficacy of protecting the nervous system, preventing Alzheimer’s disease has been satisfied.
Now there are both synthetic and natural extracted astaxanthin products available for commercial application.
|
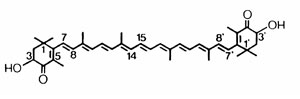 |
| The chemistry structure of Astaxanthin |
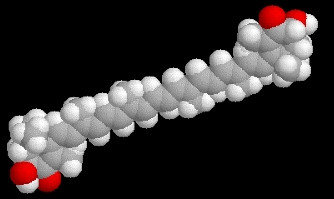 |
| The stereochemistry structure of Astaxanthin |
| |
|
What is the unique advantage of Astaxanthin in the family of Carotenoids?
The natural carotenoids was composed by plants, including more than 600 kinds of compound, such as ß–carotene, zeaxanthin, lutein, Canthaxanthin, Lycopene. Astaxanthin has an unique advantage compared to these substances which are:
Extremely strong anti-oxidation ability: Its anti-oxidation ability is 550 times than Vitamin E, 10 times than the caroenoids such as ß –carotene, zeaxanthin, lutein, Canthaxanthin, Lycopene. It is called “Super Vitamin E†or “Super anti-oxidantâ€
It could penetrate the cell membrane due to its unique chemical structure, also it could go across the blood-brain barrier and directly connected with the musculature. Thus astaxanthin has an obvious advantage of anti-oxidation for the protection of both eyes and brain, however, ß –carotene and Lycopene do not have such characteristics.
|
 |
| |
|
Sources of Astaxanthin
Since astaxanthin has great value of application and huge market potential, during the recent ten years, it has drawn more and more attention of the public. Astaxanthin is mostly existing in the body of aquatic animals, algae, fungi or bacteria, these are the potential sources of astaxanthin. At present, it is mainly gained through the following ways:
|
| |
| Chemical Synthesizing |
 |
|
It is hard to synthesize astaxanthin artificially and most of them are cis-arrangement, they could not be translated to natural trans-arrangement. The FDA only approved astaxanthin of trans-arrangement to be used as an additive for aquaculture, not allowing any kinds of chemical synthetic products to be launched on the market as health care food. The absorbing capability of animals to synthetic astaxanthin is quite weak, the capability of both pigmentation and biological potency of synthetic astaxanthin is much lower compared to a natural one. Along with the development of astaxanthin industry, these low efficient products will be eventually eliminated, however, as the output of biological source of astaxanthin has not been high enough, the chemical synthetic products are still competitive in aquaculture industry. |
| |
| The processing of abandoned shells of shellfish |
 |
|
Astaxanthin is existing in the shells of various shellfish, the abandoned shells could be utilized for astaxanthin extraction. Nowadays, there are 10 billion tons of abandoned shells from crab processing industry each year. However, the content of astaxanthin in shell is very low but the content of ash and chitin is relatively high, it has restricted the extraction of astaxanthin and the reuse of shells. Now in the country like Norway is adopting the silage technology which could reclaim the shells with high efficiency (180pg/g) and the pureness is relatively high compared to other methods of processing. However, the output is still low and the pureness is not high enough, the requirement for production is strict and the cost is high, hence only very few countries adopting this method for the production of astaxanthin. |
| |
| Fungi |
 |
|
Some fungi could be utilized to synthesize astaxanthin, such as Phaffia rhodozyma, Phadotoralarubra, Rhodotorula glutinis etc. Among which, the astaxanthin accumulation in Phaffia rhodozyma is rather high, in wild strains, it could take approximately 0.05% of the dried weight of cells, in some mutate strains it could even take 0.3%. Astaxanthin is the main component among the synthesized carotenoids, thus they have become the most commonly used strains in the production of astaxanthin by microorganism fermentation method. Phaffia rhodozyma is also regarded as the most suitable source of astaxanthin second to Haematococcus. However the accumulation of astaxanthin in this yeast could be affected by various kinds of factors under the process of fermentation. It could be altered with the alteration of zymolytic culture medium, the temperature, pH value, DO, carbon source and nitrogen source could produce big influence to it as well. Its similarity to Haematococcus is that the accumulation of astaxanthin in Phaffia rhodozyma and the growing rate of strains could be a contradiction, usually when the conditions of fermentation have to be changed in order to increase the output of synthesized astaxanthin, the yield of strains would be lowered accordingly. |
| |
|
Haematococcus
As far as we know Haematococcus is an alga in which the astaxanthin content is the highest, it is also the species which has the highest accumulation of astaxanthin among all the known organism in which astaxanthin is synthesized. The maximum accumulation of astaxanthin could take as high as 4% of the dried weight of cells. Besides Haematococcus, the chlorella, Chlamydomonas sp?Marimo?Scenedesmus?Chlorella?Snowfall Algae could accumulate astaxanthin more or less under the unfavorable conditions; The content of astaxanthin in Euglena sanguinea could also take 0.5% of the dried weight of cells. However, the shortcoming of these chlorella in which astaxanthin could be synthesized, including Haematococcus is that they grow up very slowly and always take a long period for culturing. The accumulating of astaxanthin is a product of environment stress. Under favorable conditions astaxanthin could not or rarely be synthesized. The environment stress abducting the accumulating of astaxanthin contradicts with the accumulation of biomass. During the growing period of Haematococcus, under favorable conditions Haematococcus pluvialis grows with motile, green cells that reproduce primarily by cell division. Under unfavorable conditions, for example, nutrient deficiency or drought, the cells lose their motility and form spores with tick cell walls. When transforming into this sporal phase, the alga accumulates starch and fats in its cells as energy and carbon stores. When fats are synthesized, the cells produce astaxanthin.
|
  |
| |
Green, motile stage of Haematococcus algae Red encysted stage of Haematococcusalgae
Astaxanthin functions as an antioxidant, which prevents oxidation of the fats and protects the DNA in the cell nucleus from UV radiation. The encapsulated form of the alga is called an aplanospore and in this form, the alga can survive for long periods, even under harsh conditions. Now astaxanthin from high quality Haematococcus source has taken up over 90% of the total volume of carotenoids abroad. The content is associated with quality and intensity of light. Trials showed that stronger the intensity is, the larger output of astaxanthin could be fulfilled and the result of a continuous light will be better than a interrupted one.
|
 |
| Haematococcus which has been harvested from culturing ponds, Hawaii |
| |
|
Different value of Astaxanthin from different sources
Natural Astaxanthin --- Power
Different sources of astaxanthin has different stereoisomer
|
 |
|
Perhaps the most vigorous endurance feat in the animal world is the migration up raging rivers by salmon. Salmon accumulate trans-astaxanthin in their muscles, which explains their red-orange color. Scientists inferred from this phenomenon that the high level of trans-astaxanthin endow the salmon with the ability of migration up raging rivers without any hesitation.
Most artificially synthesized astaxanthin are cis-arragnement, and they could not be translated to natural trans-arrangement in an animal’s body. The absorbing capability of animals to synthetic astaxanthin is quite weak, the capability of both pigmentation and biological potency of synthetic astaxanthin is much lower compared to a natural one. |
| |
| Different sources astaxanthin molecule has different type of compound |
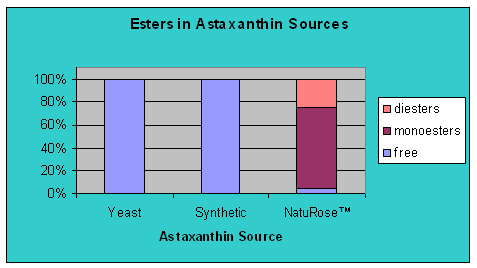 |
|
Generally to say, compared the ester astaxanthin to free astaxanthin, it has higher stability as well as lipid solubility, hence is could be easier for human absorbing. |
| |
| Different source astaxanthin has different geometric structures: |
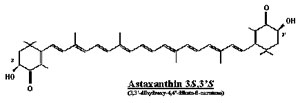 |
| levo-astaxanthin |
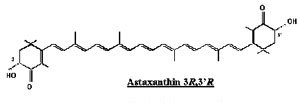 |
| dextro-astaxanthin |
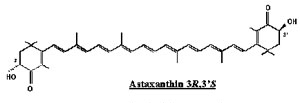 |
| Meso-astaxanthin |
| |
| Three possible geometric strictures of astaxanthin |
|
Synthesized Astaxanthin |
25% levo-astaxanthin, 25% dextro-astaxanthin,
50% meso-astaxanthin, |
| Phaffia rhodozyma Astaxanthin |
Pure dextro-astaxanthin, |
| Haematococcus source astaxanthin |
Pure levo-astaxanthin | |
| |
|
According to the research result from FDA, the astaxanthin in the bodies of 6 kinds wild captured salmon is mainly levo-astaxanthin, thus natural astaxanthin must has outstanding value. |
| |
| Natural astaxanthin --- Haematococcus extracts BioAstin® |
 |
|
BioAstin® are produced by the biggest algae products manufacturer in the world --- Cyanotech Inc. USA, one of the listed companies of Nasdaq. Cyanotech is the biggest producer of high quality natural astaxanthin in the world and the pioneer of the technology. It possesses 80 acres of natural culturing fields on ancient lava, located on the Island of Kona, Hawaii. The specialized Haemtococcus has a very strict quality control process during culturing, it is cultivated in a patented closed system. The extraction is made by super-critical CO2 extraction instead of organic solvent extraction, in this way, highly concentrated and activated astaxanthin could be obtained. The whole process of production and their products are in conformity with FDA authentication as well as GMP standard, hence the high quality of natural astaxanthin could be ensured. |
| |
 |
| A corner of Kona Island, Hawaii --- the airscape of Haemtococcus culturing fields of Cyanotech |
| |
 |
| 85 culturing ponds, stable sunlight and temperature, all year round production |
 |
| Clean air and water source, an ideal place for pure algae production |
| |
|
Efficacy and characteristics
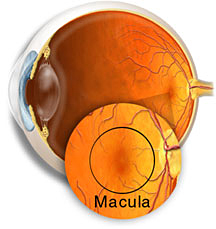
Protection for eyes and central nerve system
|
 |
|
The photoreceptor cells contain the highest concentration of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA’s) of any tissue in the human body. Thus, when high-energy blue light waves interact with the retina, singlet oxygen and other excited oxygen species are formed through photooxidation causing peroxide damage to the lipids. For human and animals, the carotenoids in their diets for eyes protection is necessary, as it could quench the harmful active oxygen, protecting retina through the anti-oxidation process. In clinic, it could be applied for the therapy of age-related macular degeneration. A recent clinical research result has shown that astaxanthin is able to readily cross the blood-brain barrier and protect the retina against photo oxidation and loss of photoreceptor cells. It has showed that astaxanthin has satisfied efficacy for the prevention of age-related macular degeneration and improving the function of retina. |
| |
| |
|
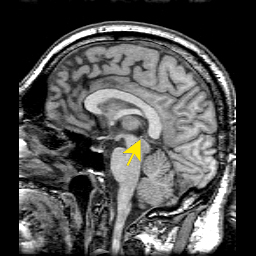
The central nerve system (including the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerve) contains abundant unsaturated fatty acid and iron. Its metabolic activity is high and easily be damaged by oxidation, causing various disease of nerve system. Astaxanthin has the function of protecting the central nerve system, especially to the brain and spinal cord. For ischemia-reperfusion injury, spinal cord injury, Parkinson’s Disease, Alzheimer’s Disease and other injuries associated with central nerve system, it could effectively treated. |
 |
| |
| Preventing UV radiation |
 |
|
Ultraviolet radiation has long been known to cause epidermis photoaging and skin cancer. The research has indicated that astaxanthin exerts a specific action on transglutaminase enzymes to consume these polyamines in response to skin irradiation. Moreover, astaxanthin also had a stronger inhibitory effect on putrescine accumulation than dietary retinal. That means the activation of astaxanthin provides a potential protection for light and preventing the skin from photoaging. Astaxanthin could effectively eliminate the radiation of computers, environmental pollution, free radicals derived from smoking which could cause the skin to be aged, protecting the mitochondrion membrane from being damaged by oxidation thus all the cells could be protected from being damaged by oxidation. |
| |
| Anti-Cancer |
 |
|
The research results of anticancer active immunology indicated that the oral taking of carotenoids has a certain effect of anti-cancer, it could produce influences directly on immune system causing the knub to be shrank. Feeding the rats with astaxanthin for trial, the result showed that it could obviously restrain the cancer caused by chemicals on early stages. For the epithelia which is exposed to carcinogen, it showed an effect of anti-proliferation and immune system enhancing as well as a dose response. We could infer that astaxanthin has a strong ability of anti-cancer. It induces the enzyme in liver to restrain the cystic cancer, buccal cancer, colonic cancer and stomach cancer of the rats, more effective than beta-carotene. The oral taking of astaxanthin could also restrain the mammary cancer, the dose response is not existed neither in beta-carotene nor canthaxanthin. Astaxanthin could reduce the carcinogenic effect of aflatoxin, the results of reducing both the quantity and volume of liver knub cells caused by aflatoxin have been very good. Recently, researchers mentioned the anticancer mechanism of astaxanthin that it is associated with the stability of cells membrane and the gene of conexin-43. Through changing the numbers of conexin-43 to regulate the communicating between the cells in order to improve the balance between the cells, sustaining the normal function of cells. Another research on rat’s cells of liver has shown that astaxanthin could induce the composition of xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes (XME), this process has closely connected with anti-cancer as well (Gradeletetal, 1996). The natural killer cell (NK) has a crucial effect in terms of anti-cancer and restraining the metastasis of a carcinoma. According to Kurihara’s idea (2002), astaxanthin could restrain the damage of anti-cancer capability of natural killer cells caused by environmental stress, therefore, it could restrain the metastasis of a carcinoma |
| |
| Anti-inflammation characters |
 |
|
The aches of joints and arthritis are usually caused by the injury of oxidation from free radicals. The appearance of free radicals is due to the fact that the body is exposed to toxic air or immune reaction problems. The strong anti-oxidation character of astaxanthin could assist to restrain the producing of free radicals and reducing the injury of joints from oxidation. A new research result of anti-infection showed that when the rats are fed with Haematococcus source astaxanthin powder, the attaching and infection of Helicobacterpylori on stomach are obviously reduced. Thus in some countries, the oral use of astaxanthin has been developed for anti-infection purpose. The diester-astaxanthin could be used combining with other anti-infection drugs, when it is served with aspirin, the effect could be enhanced. |
| |
|
Releasing fatigue of sports
Astaxanthin could strengthen the power and endurance of muscles,releasing fatigue of sports rapidly,reducing the DOMS after acute exercises. When muscles work, free radicals are released and these can cause oxidative stress if not dealt with by antioxidants, it could cause aches or injury of muscle tissues. Intense aerobic exercise leads to the production of reactive oxygen species(ROS) through a variety of mechanisms. These exercised induced ROS oxidize several targets such as proteins, lipids and DNA causing damage to skeletal muscle, heart and liver. Also a secondary inflammatory response is generated that adds to delayed-onset muscle damage induced by ROS. Previous studies demonstrated that antioxidants like vitamin E, C and carotenoids can decrease oxidative damage. A recent result of research has shown that astaxanthin has obvious effect on releasing fatigue.
|
 |
| |
|
Preventing Cardiovascular diseases
The clinical research associated with prevention of atherosclerosis shows that oxidation of LDL is an important reason of causing atherosclerosis. If the concentration of LDL in someone’s body is high, he or she could take higher risk of suffering from atherosclerosis, the wall of blood vessel of artery will be damaged at the same time. Moreover, as the blood platelets aggraded, the blood vessels will become thinner and finally it could block the blood flow in artery which will cause heart disease or apoplexy. On the other hand, if the concentration of HDL in blood is relatively high, the risk of coronary artery disease will be decreased, thus it could prevent atherosclerosis. Astaxanthin could increase the content of HDL but decrease the LDL in the body, but neither beta-carotene nor canthaxanthin has such an effect, that means astaxanthin could reduce the oxidation of apolipoprotein and the application for preventing atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease and ischemic encephalopathy is possible.
|
 |
| |
Function and mechanism
Free radicals & Health
As everybody knows that the environment is being polluted more and more seriously and people’s habits of diets as well as life style are changing, a lot of free radicals could be produced in the body which could easily cause various diseases and damaging the organs. However, what is free radicals? Let’s have an example, as we know, the iron could be rusted in the air, that is due to the effect of long period of sunshine and raining, also varieties of acid substances in rain water which could oxidate the iron. In case the iron could not be dealt with measures of anti-rust, it could be corrupted very quickly. The metabolism of human body is similar to the oxidation process of the iron, in other words the so-called “rusting†phenomena happens every day in human body. It is called “free radicals†in technical terms of medicine. The free radicals are very harmful to human body, mainly injuring the cells in organic body. Under normal conditions, free radicals are of little harmful since the human body could produce some certain substances to resist them. However, when the concentration of such substances in human body drops, the balance is broken and the ability of anti-free radical will be reduced which could cause a lot of diseases such as aging, Meniere’s Disease, atherosclerosis, bacteria meningitis, cerebrovascular disease, age-related macular degeneration, Parkinson’s Disease, ocular meningitis, nerve system diseases, etc.
Such being the case, we have to improve the ability of quenching free radicals by supplementing natural anti-oxidation products, astaxanthin has been the first choice based on its strong efficacy.
The mechanism of anti-oxidation
In 1956 Rebecca Gerchman and Daniel Gilbert detected toxic effect of superoxid on aerobs. Till today there are identificated many free radicals. Their toxic effect is registrated in more than 100 diseases (malign diseases, arteriosclerosis, AIDS, arthritis...)
Antioxidants are molecules which can safely interact with free radicals and terminate the chain reaction before vital molecules are damaged. In organism they are found intracellular and extracellular. Many substances have the ability of anti-oxidation, such as vitamin C, vitamin E and carotenoids, etc.
Astaxantin is isolated for the first time in 1938 from sea crab (lobster). Astaxantin is one of the most potent natural antioxidants. It protects cells against oxidation by quenching single oxygen scavenging free radicals and effectively breaks peroxide chain reactions.
Comparison of ability for anti-oxidation
The research has shown that astaxanthin has the ability of anti-oxidation 10 times than beta-carotene, 60 times than OPC, 550 times than vitamin E. In terms of ability of quenching oxygen molecule, the order should be: astaxanthin >a-carotene > ß-carotene > Bixin > zeaxanthin > lutein > Bilirubin > biliverdin
|
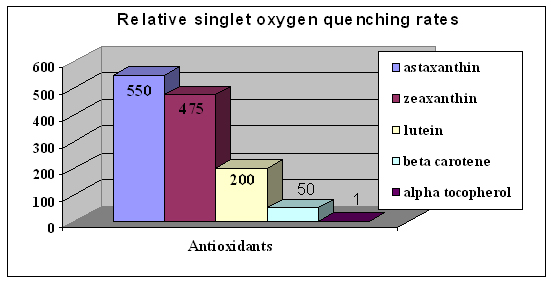 |
| |
Range of application
At present, natural astaxanthin is widely developed in some countries as advanced nutritious health card food and drugs for human application, mainly aiming at its function of immune system enhancing, anti-cancer, protecting retina from being damaged by UV and light oxidation, anti-inflammation, preventing injury of oxidation of blood LDL-cholesterin.
The products of Twinlab Inc. USA is for Joint Health and Mobility; Cyanotech’s BioAstin and Astafactor Sports Formula of Aquasearch Inc could benefit the joints, releasing fatigue of sports. Astafactor Salmon Essentials produced by Aquasearch Inc is specially for cardiovascular health. One company in Hawaii is developing a drug for myocardial infarction treatment; another biological company has launched a sun block softgel and cream, using astaxanthin for UV radiation protection. There are also two of external use products as well as some anti-inflammation formulated products including drinks containing astaxantin for UV radiation protection have been developed in Japan. The series of cosmetics produced by Natureal and Astacure are containing astaxanthin as well.
|
 |
| |
| Practical Application |
 |
For Health Care(BioAstin®) |
 |
Retarding the process of aging | |
| |
|
Suggested ingredients: Antaxanthin 2.5mg/gel, rice bran oil, natural gelatin, plant source glycerin.
Function: Pure natural anti-aging food, the ability of anti-oxidation is 100-500 times than Vitamin E. Effectively eliminate the free-radicals in the body and retard the process of aging from the cell level, ensuring the activity of each cell.
Nourishing the skin
Suggested Ingredients: Natural Astaxanthin oil 1mg, Alpha-Lupaline 0.12ml
Function: Providing enough nutrition and protection to the skin, making the skin to be flexible, smooth and cleanlily. Astaxanthin could provide varieties of anti-oxidation protection. The omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acid essential oils in Alpha-Lupaline could eliminate toxic substances in the body and preventing inflammation |
 |
| |
 |
Anti fatigue associated with sports
Suggested Ingredients: Astaxanthin 4mg, high oleic safflower oil, natural gelatin, glycerin.
Function: Effectively reduce the ache on muscle and joints due to the acute exercises, releasing fatigue rapidly after sports, prevent musculature from being damaged due to acute exercises.
Similar Product: BioAstin produced by Cyanotech. 60 gels/bottle. |
|
|
|
|
 |
Ease Rheumarthritis
Suggested Ingredients: Haematococcus extract (natural astaxanthin), Chondroitin sulphate etc.
Function: Keep the balance of free-radicals in body, releasing aches caused by rheumarthritis |
|
|
 |
Cardiovascular Diseases
Suggested Ingredients: astaxanthin 1.33mg , Vitamin E 20000 IU, 0.226g EPA and 0.144g DHA
Function: Lowering the LDL in blood, preventing atherosclerosis and protecting cardiovascular system. |
|
|
 |
Suntan Prevention (Oral)
Suggested Ingredients: Haematococcus extract, yeast essentials, Vitamin C, Kawatani powder, liquorice essentials, nucleic acid, Vitamin B2, Vitamin E.
Function: Protecting the skin from being aged due to the UV radiation, avoiding melanin deposition, prevent cancer. |
|
|
 |
Multiple Vitamins
Suggested Ingredients: Astaxanthin 0.1-0.5 mg, other vitamins.
Function: Providing over-all nutrition and protection to brain, eyes, skin, immune and circulation system. | |
| |
 |
| |
 |
Anti-oxidation --- Astaxanthin capsules
Suggested Ingredients: Astaxanthin 1 mg, micocrystalline cellulose, natural gelatin, glycerin.
Function: The most effective natural anti-oxidation vitamin, providing an over-all protection for the body from being damaged by free radicals, maximized the utility of carotenoids and vitamins in the body. |
| Cometics(BioAstin®) |
|
|
 |
Lipsticks
Suggested Ingredients: Alfalfa, Haematococcus extract, bilberry, avocado oil, wintergreen oil
Function: Preventing lips from being damaged by UV radiation, pure natural components, plant source extracts, non-toxic and no stimulation to skin |
|
|
 |
Facial essence gel
Astaxanthin content: 0.02% of Haematococcus extract
Suggested Ingredients: Haematococcus extract, rice bran sphingoglycolipid, amino acid.
Function: Haematococcus extract originated from Hawaii, preventing the deposition of melanin and reducing freckles, retaining moisture and keeping the skin to be more flexible. | |
|
|
 |
 |
Anti-wrinkle cream
Astaxanthin content: 0.07% of Haematococcus extracts. | |
| |
| Suggested Ingredients: |
 |
Haematococcus extracts, evening primrose extracts, Water soluble collagen, Vitamin E and Vitamin C. |
|
|
 |
Buckthorn, Alpha-Lupaline, purifed oil of apricot kernel, astaxanthin oil
Function: Haematococcus extract originated from Hawaii, the strongest anti-oxidant vitamin in nature, the anti-oxidation ability is 100-500 times stronger than Vitamin E. It could reduce the harmful free radicals in human body to the minimum, retarding the aging of cells and anti-wrinkle, making the skin to be more flexible and sleek. | |
| |
 |
| Sun block |
Astaxanthin content: 0.06% of Haematococcus extracts.
Suggested Ingredients: Haematococcus extracts, aloe extracts, orange extracts, cucumber extracts, folic acid, vitamin A, C and E, zinc oxide
Function: Quenching free radicals caused by UV efficiently relying on the unique structure of natural astaxanthin. Preventing skin from photoaging and reducing the damage to the skin from UVA and UVB, as well as skin cancer. |
 |
| |
| Patents Associated With Astaxanthin |
| Patent number |
Company |
Patent tittle |
|
EP0786990 |
Us nutraceuticals |
Use of astaxanthin for retarding and ameliorating centralnervous system and eye damage |
|
EP1217996 |
Astacarotene |
Use of astaxanthin for treatment of autoimmune diseases,chronic viral and intracellular bacterial infections |
|
US6475547 |
Astacarotene |
Immunoglobulin-rich milk, production and use thereof |
|
WO0023064 |
Astacarotene |
Treatment of dyspepsia |
|
US6410602 |
Astacarotene |
Method of increasing the production and improving the quality of semen |
|
US6335015 |
Astacarotene |
Method of the prophylactic treatment of mastitis |
|
US6262316 |
Astacarotene |
Oral preparation for the prophylactic and therapeutic treatment ofhelicobacter sp. Infection |
|
US6245818 |
Astacarotene |
Medicament for improvement of duration of muscle function or treatmentof muscle disorders or diseases |
|
US6054491 |
Astacarotene |
Agent for increasing the production of/in breeding and production mammals |
|
US5744502 |
Astacarotene |
Method for increasing the production of/in breeding and productiona nimals in the poultry industry |
|
US6433025 |
Cyanotech |
Method for retarding and preventing sunburn by uv light |
|
US6344214 |
Cyanotech |
Method for retarding and ameliorating fever blisters and canker sores |
|
US6258855 |
Cyanotech |
Method of retarding and ameliorating carpal tunnel syndrome |
|
EP1283038 |
Suntory ltd |
Compositions normalizing circadian rhythm |
|
WO03013556 |
Itakura hiroshige |
Medicinal compositions having effects of amelioratingeye diseases and holding eye functions |
|
WO03003848 |
Aanesen berit annie |
The use of di-esters of astaxanthin for enhancing the growth offarmed fish |
|
WO02094253 |
Fuji chem ind co |
Agents for relieving eye controlling function error |
|
KR2000045197 |
Pacific co ltd |
Healthy nutrition composition containing chitosan oligosaccharideand astaxanthin |
|
WO02058683 |
Lycored |
Carotenoids as anti-hypertension agents |
|
NZ299641 |
Suntory and itano |
Use of astaxanthin in pharmaceuticals for treating stress |
|
US6277417 |
Triarco |
Method of inhibiting 5alpha-reductase with astaxanthin |
|
US2003/778304 |
Anderson and petterson |
Method of inhibiting the expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines |
|
JP10276721 |
Suntory and itano |
Astaxanthin-containing food or drink | |
| |
| Our natural astaxanthin products line |
 |
Natural astaxanthin softgel |
|
|
 |
Natural astaxanthin beadlets(1.35%) |
|
|
 |
Natural astaxanthin oleoresin(5%) |
|
|
 |
Natural astaxanthin oleoresin(7%) |
|
|
 |
Natural astaxanthin algae powder(1.5%) | |
| |
 |
| |
| Natural astaxanthin softgel BioAstin® |
|
The unique astaxanthin softgel in the world made of natural micro-algae extracts for the time being. Astaxanthin is a kind of carotenoids which has very strong ability of anti-oxidation. It has been honored as the strongest vitamin for anti-oxidation. The astaxanthin component in this product is derived from the algae Haematococcus which grows by the seaside of Hawaii, it is a pure natural product without any animal source components and Non-GMO. The softgel is containing safflower seed oil as well in which the Linoleic content is as high as 73%-85%, it is called “king of Linoleicâ€. It could promote the transferring and exhausting of cholesterol, improving the distribution of cholesterol in the body.
Function of Astaxanthin:
Various trials showed that the ability of anti-oxidation of astaxanthin is 550 times than vitamin E and 10 times than beta-carotene.
Various clinical trials on human body showed that astaxanthin has outstanding efficacy on the following aspects:
Quick releasing of fatigue caused by sports, preventing damage of muscles and bones;
Releasing joints ache caused by rheumarthritis
Preventing skin from being damaged by UV radiation
Protecting eyes and central nerve system
Lowering the LDL in blood, preventing cardiovascular system diseases
Enhancing immune ability, preventing cancers
Main Ingredients:
Each gel containing 50 mg of Haematococcus extracts, (natural astaxanthin content not lower than 4 mg), safflower oil 440 mg and vitamin E 10 mg
Suitable group: Seniors, sports amateurs, etc
Suggested dosage: 1'2 gels per day with the meal
Method for storage: Cool and dry place.
Quality guarantee period : 24 months
|
| |
| BioAstin® Natural Astaxanthin tablet-grade beadlets |
Description: Dark red lipid extract of Haematococcus pluvialis microalgae encapsulated into tablet-grade gelatin beadlets. Contains minimum of 1.35% astaxanthin by weight plus other mixed carotenoids, natural vitamin E and vitamin C.
Particle size: 100% through No.20 U.S. Standard Sieve (<850 micron).
Regulatory Status: Haematococcus algae astaxanthin has been FDA-reviewed and allowed as a dietary supplement (August 1999). This product is free of genetically modified organisms (GMO) and ingredients. The gelatin used in these beadlets is certified BSE-free. |
| |
| General Composition: |
|
Astaxanthin |
>1.35% |
|
Total lipids |
18% |
|
Carbohydrate |
29% |
|
Protein |
45% |
|
Moisture |
7% |
|
Ash |
<1% |
|
Lead |
<1 ppm |
|
Cadmium |
<0.5 ppm |
|
Arsenic |
<1 ppm |
|
Mercury |
<0.025 ppm | |
| |
| Quality Control: |
|
Total aerobic bacteria |
<1,000 cfu/gram |
|
Total coliforms |
<10 cfu/gram |
|
E. coli |
negative |
|
Salmonella |
negative |
|
pesticides |
negative | |
| |
|
Astaxanthin Determination:
Minimum 1.35% astaxanthin by weight. Additional carotenoids naturally present may include beta-carotene, lutein and canthaxanthin. HPLC, Cyanotech Technical Bulletin Ax-015; method accepted by U.S. Food and Drug Administration and Canadian Food Inspection Agency.
Stability: For maximum stability store below 8°C and use within one year of receipt. Stability within tablet will depend upon customers formulation and packaging. Cyanotech recommends the use of oxygen absorbers or nitrogen-purge and PETE or glass packaging with inductively sealed caps.
Application:
For the production of health care food such as capsules or tablets;
Component for functional food and medicine production;
Functional ingredient for cosmetics.
|
| |
 |
| |
Natural Astaxanthin oleoresin BioAstin®
Two kinds of natural astaxanthin oleoresin, the content of astaxanthin is 5% and 7% saperately.
Description: Dark red lipid CO2 extract of Haematococcus pluvialis microalgae containing 5% natural astaxanthin plus other mixed carotenoids. Standardized with high oleic safflower oil.
|
| |
| General composition: |
|
Total Astaxanthin |
Guaranteed Minimum 5% |
|
Total Carotenoids |
Typical 5.5% |
|
Total Lipids |
Typical 21% |
|
Carbohydrates |
Typical 21% |
|
Protein |
Typical 0.5% |
|
Moisture |
Typical 3.5% |
|
Calories |
Typical 7.5 per gram | |
| |
| Typical carotenoid composition(% of extract): |
|
Astaxanthin, all-trans |
4.05 |
|
Astaxanthin, 9-cis |
0.82 |
|
Astaxanthin, 13-cis |
0.43 |
|
Astaxanthin, 15-cis |
0.02 |
|
Astaxanthin, di-cis |
0.05 |
|
Astacene |
0.23 |
|
Semi-Astacene |
0.21 |
|
Beta-Carotene |
0.08 |
|
Canthaxanthin |
0.09 |
|
Lutein |
0.05 | |
| |
| Typical carotenoid composition(% of extract): |
|
Gamma linolenic |
0.4 |
|
Linolenic |
3.5 |
|
Oleic |
14.0 |
|
Stearic |
1.7 |
|
Palmitoleic |
0.5 |
|
Palmitic |
7.5 |
|
Linoleic |
43.9 |
|
Total saturated fat |
9 |
|
Total mono-unsaturated fat |
15 |
|
Total poly-unsaturated fat |
48 | |
| |
| Regulatory status: FDA-reviewed and allowed as dietary supplement (August 1999). Ingredients contain no genetically modified organisms (non-GMO). No animal ingredients. |
| |
| Quality control: |
|
Total aerobic bacteria |
<1,000 cfu/gram. |
|
Total coliforms |
<10 cfu/gram |
|
E. coli |
negative. |
|
Heavy metals: arsenic, cadmium, lead and mercury |
<1 ppm each |
|
Pesticides |
negative | |
| |
|
Astaxanthin determination:
HPLC, Cyanotech Technical Bulletin Ax-020. Method validated by U.S. Food and Drug Administration and Canadian Food Inspection Agency.
Stability: 1 year from shipment date. Store below 8°C.
Application:
For the production of health care food such as softgels;
Component for functional food and medicine production;
Functional ingredient for cosmetics.
|
 |
| |
FAQ
Q. What are the advantages of Haematococcus source astaxanthin?
A. Pure natural plant source; the structure of astaxanthin is the same with that in the body of salmon and lobster; CO2 extract without remains of organism solvent; maximum content of astaxanthin.
Q .How about the safety for human consumption of astaxanthin?
A. Haematococcus pluvialis algae has been reviewed by the US Food and Drug Administration and cleared for marketing as a new dietary ingredient and as a feed additive in the aquaculture; It is also been approved in Japan for use in both foods and animal feeds. It has been approved as a feed additive for salmonids by the Canadian Food Inspection Agency. Similar registrations are in progress in the European Union. Varieties of Haematococcus source nutritious food and cosmetics have been widely consumed in Europe, USA and Japan.
Q. What are my formulation options for BioAstin?
A. BioAstin is offered as a standardized 5% and 7% astaxanthin oleoresin or as a stabilized beadlet for tableting. Should you prefer a gel cap we can direct you to encapsulation partners who have experience with BioAstin.
Q. Does astaxanthin have vitamin A activity?
A. No. The body does not convert astaxanthin to vitamin A.
Q. In some situations beta-carotene can form a pro-oxidant state (helping to form free radicals)with high dosages not recommended for smokers. Does astaxanthin exhibit this characteristic?
A. No. Astaxanthin has been characterized as a pure antioxidant. Although astaxanthin is considerably stronger as an antioxidant than beta-carotene, it does not form a pro-oxidant state. Dosages exceeding 40 mg per day have shown no adverse effects.
Q. Is BioAstin safe for people with shellfish allergies?
A. Absolutely. BioAstin is derived from pure cultures of a fresh water alga and does not contain shellfish allergens.
Q. Is astaxanthin from yeast the same as that contained in BioAstin?
A.No. The astaxanthin in BioAstin is identical to the form found in nature while the yeast form is chemically different from the natural form. Be sure also to check regulatory and stability issues when reviewing other sources.
|
| |
 |
| | |
|